Rotary Valves
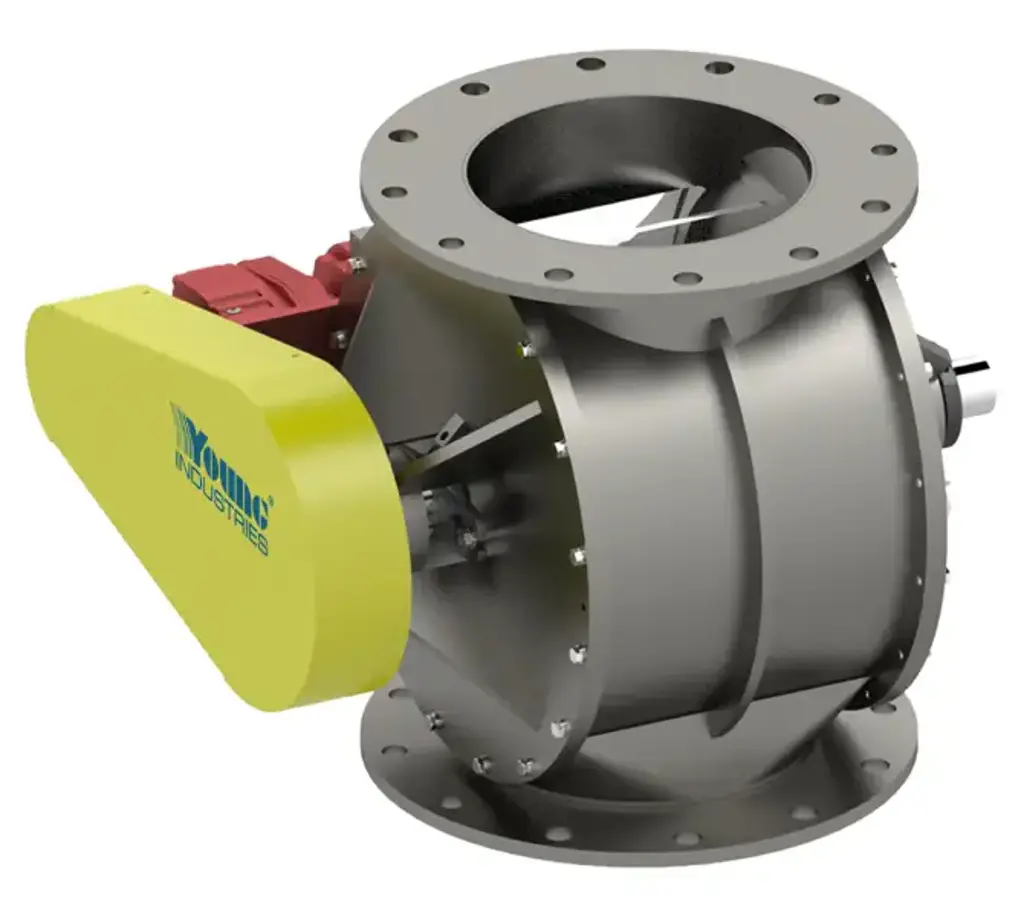

Keep your materials moving and your processes running smoothly with Young Industries' Rotary Valves. Backed by over 55 years of experience, our valves are designed to handle a wide range of bulk materials, from fine powders to pellets and chips.
We understand that every application is unique. That's why we offer a diverse selection of rotary valves, each engineered to address specific challenges and deliver optimal performance. Whether you need high-capacity feeding, precise metering, or airtight sealing, we have the solution for you.
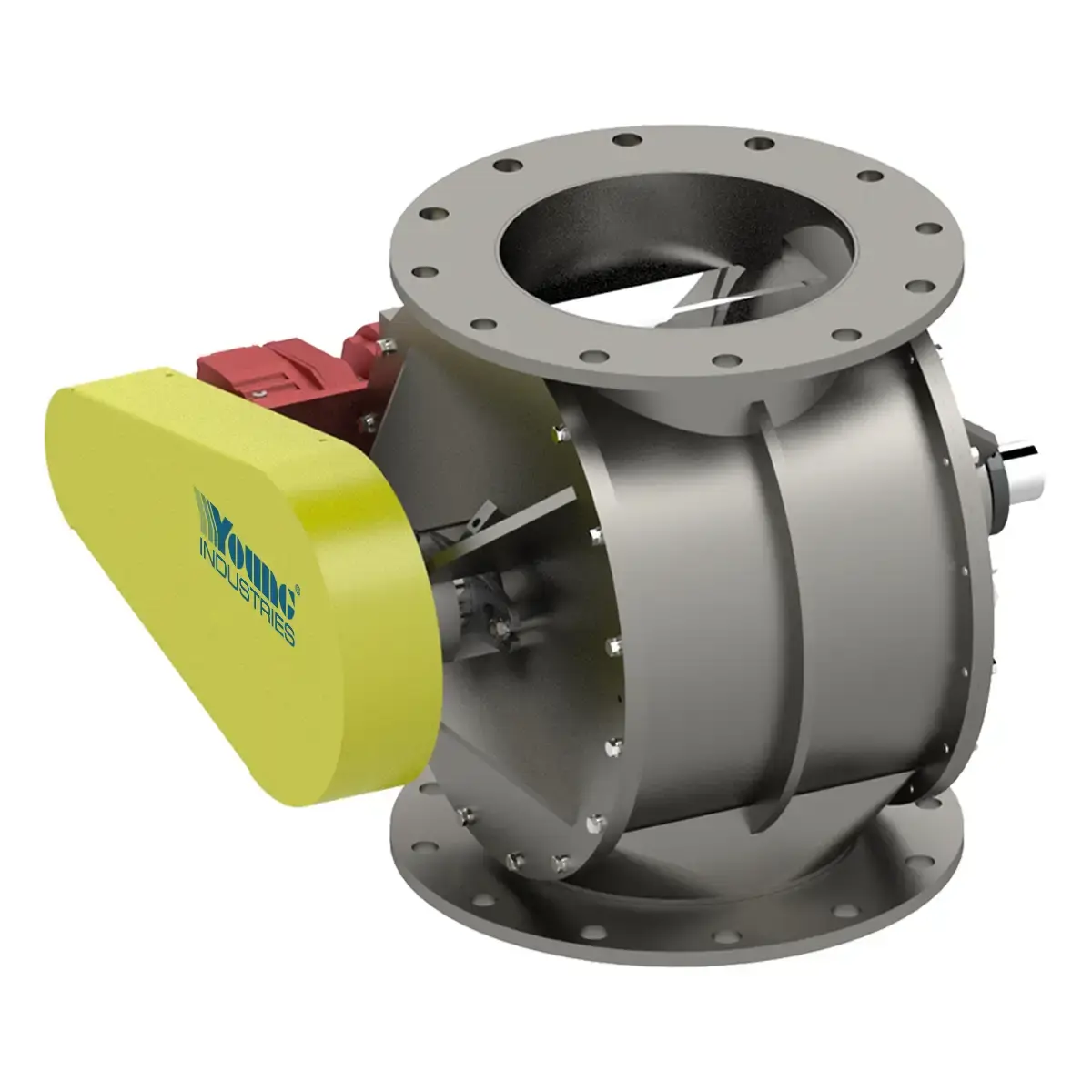

Model HC
The industry's most reliable high-capacity, low-leakage rotary valve.Contact Young Industries today to learn more about our products.
Learn More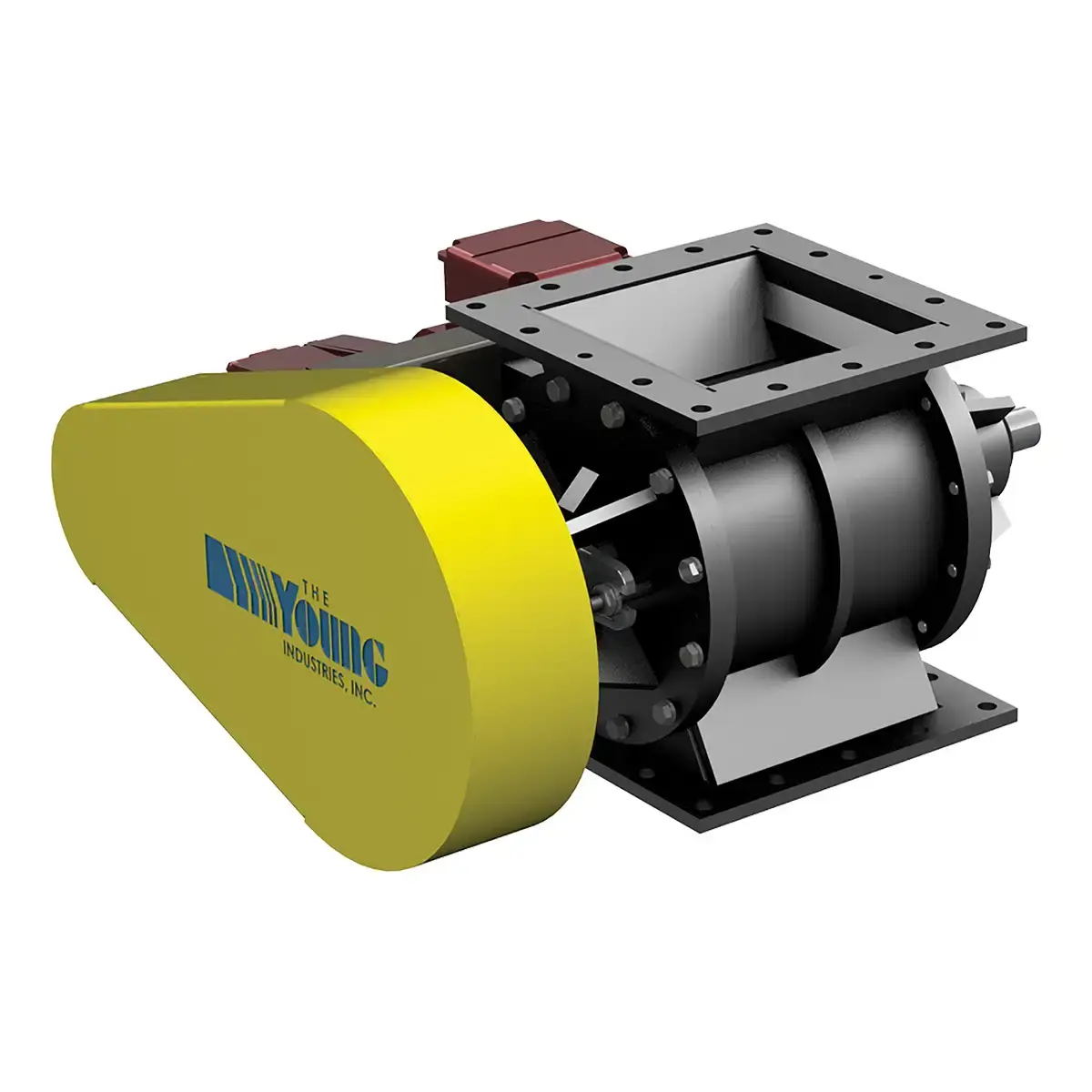
Model LH
The Model LH Rotary Valve is a low-headroom rotary airlock feeder valve designed for applications where space is limited. Learn more!
Learn More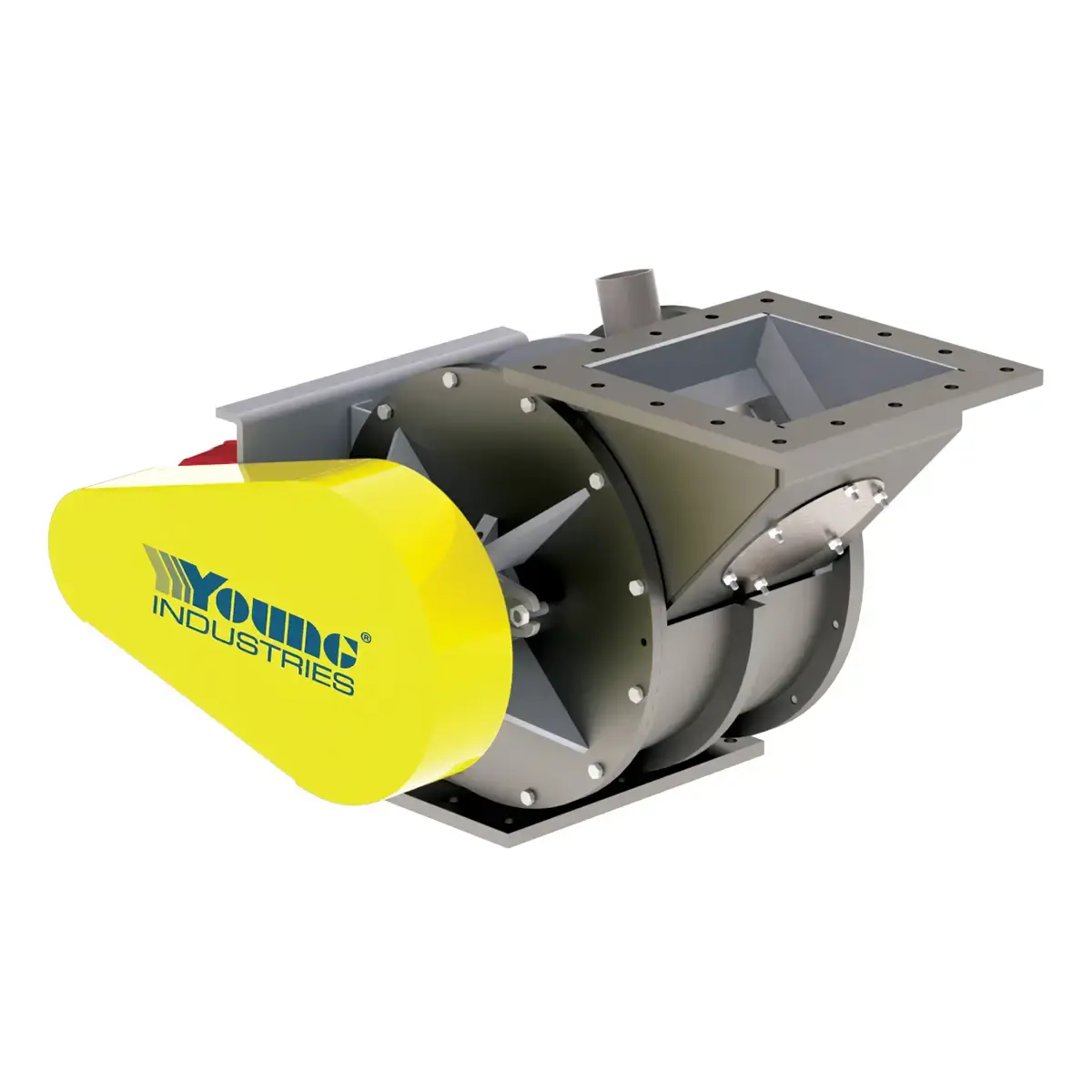
Model SE
Prevent pellet jamming and ensure precise metering with Young Industries' Model SE Rotary Valve.
Learn More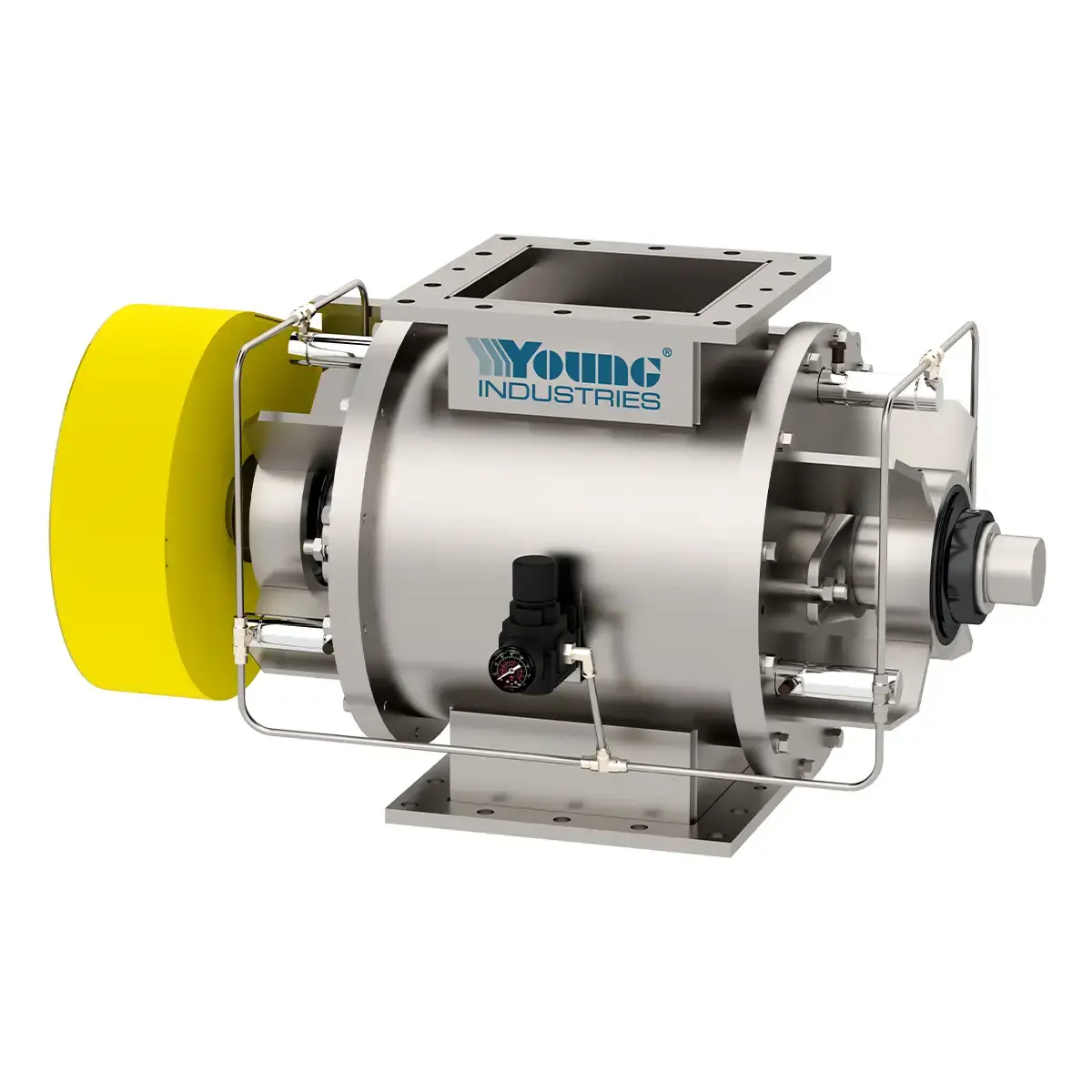
Model ES
Slash air leakage by 50% with Young Industries Model ES End Seal Rotary Valves. Available in HC, LH, and SE models.
Learn More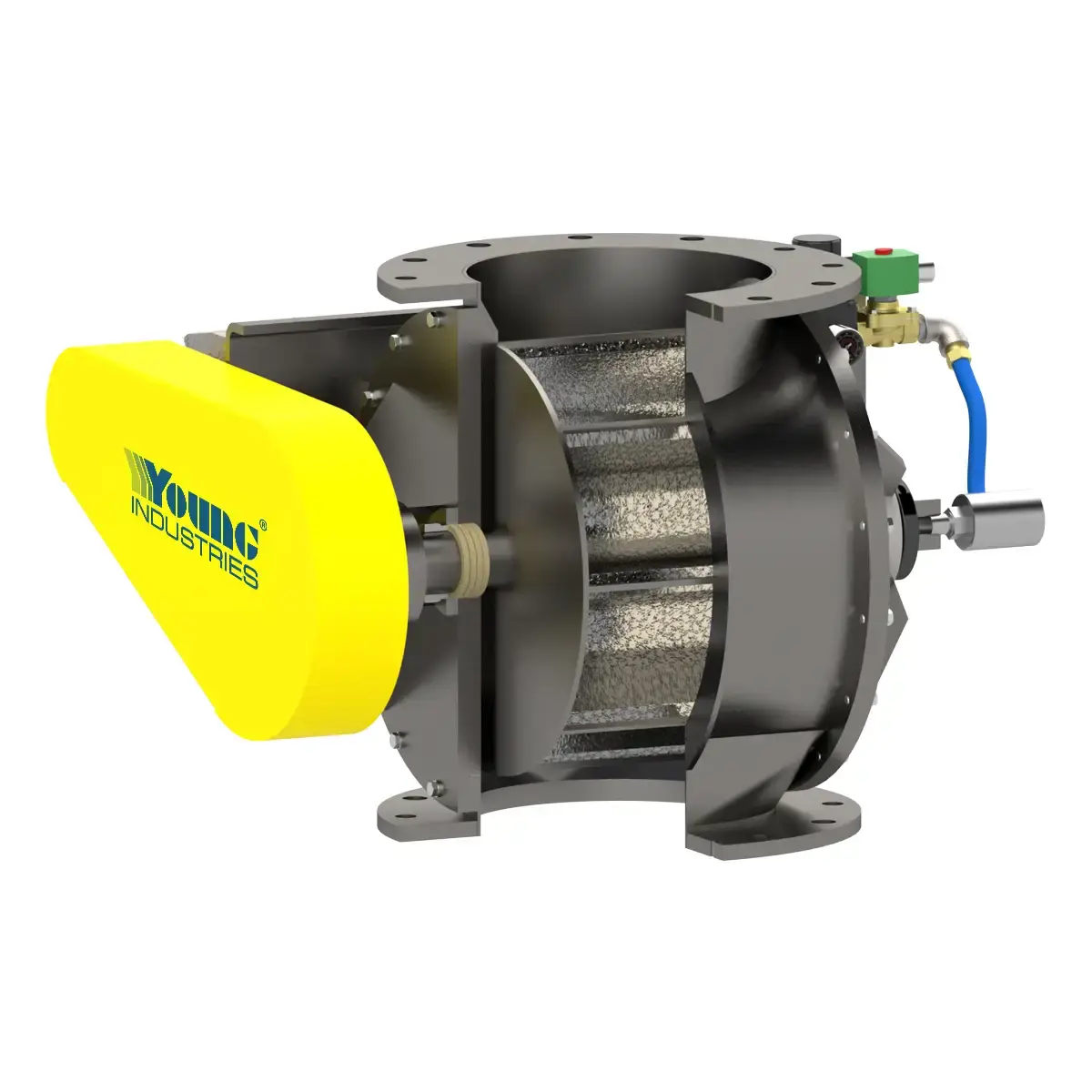
Model EV
Precisely meter cohesive battery materials with the Model EV Rotary Valve. TransFlow® technology ensures smooth flow, even with challenging powders.
Learn More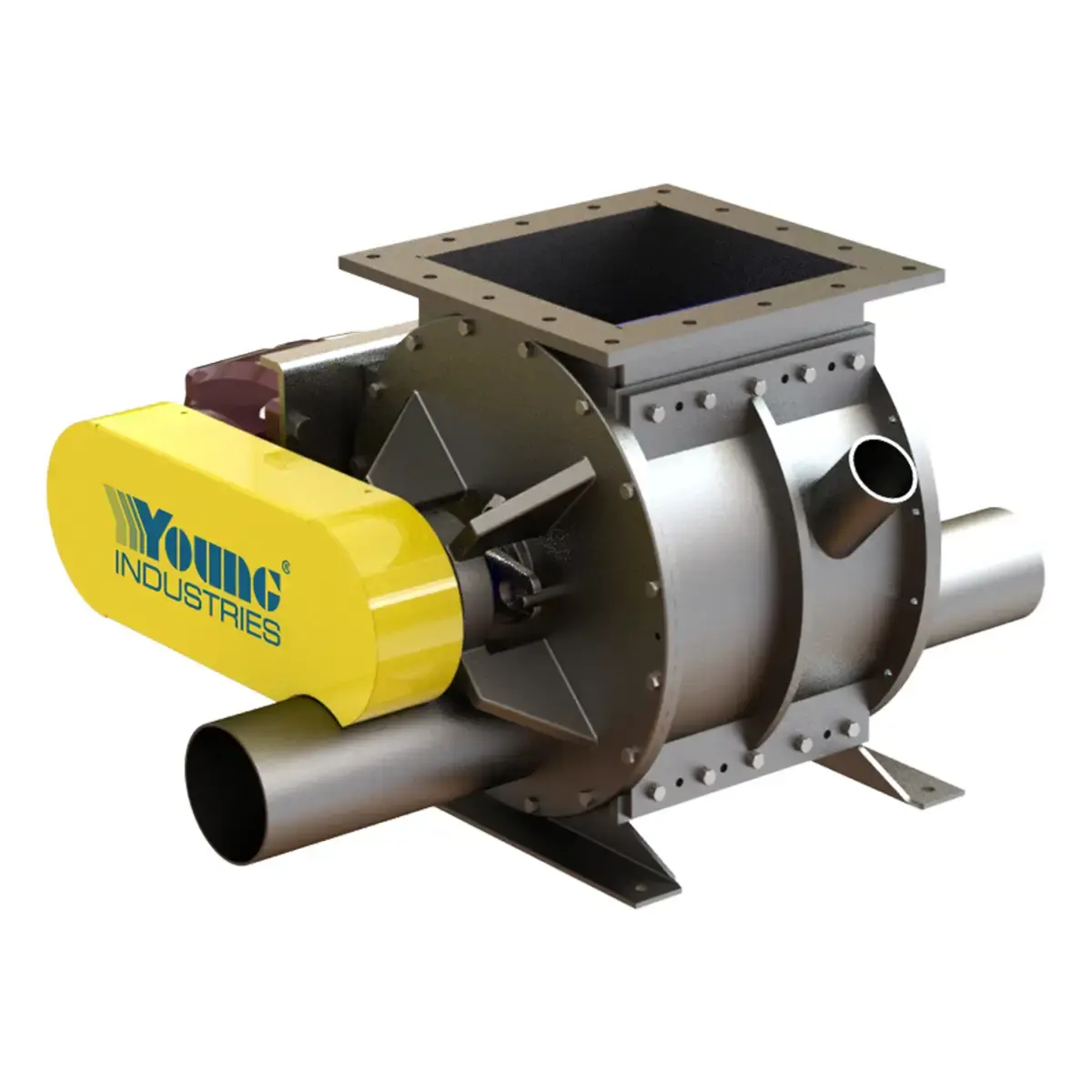
Model BT
Model BT (Blow-Thru) Rotary Valves offer compact design, air-assisted discharge, and customizable features to ensure efficient, reliable material handling.
Learn More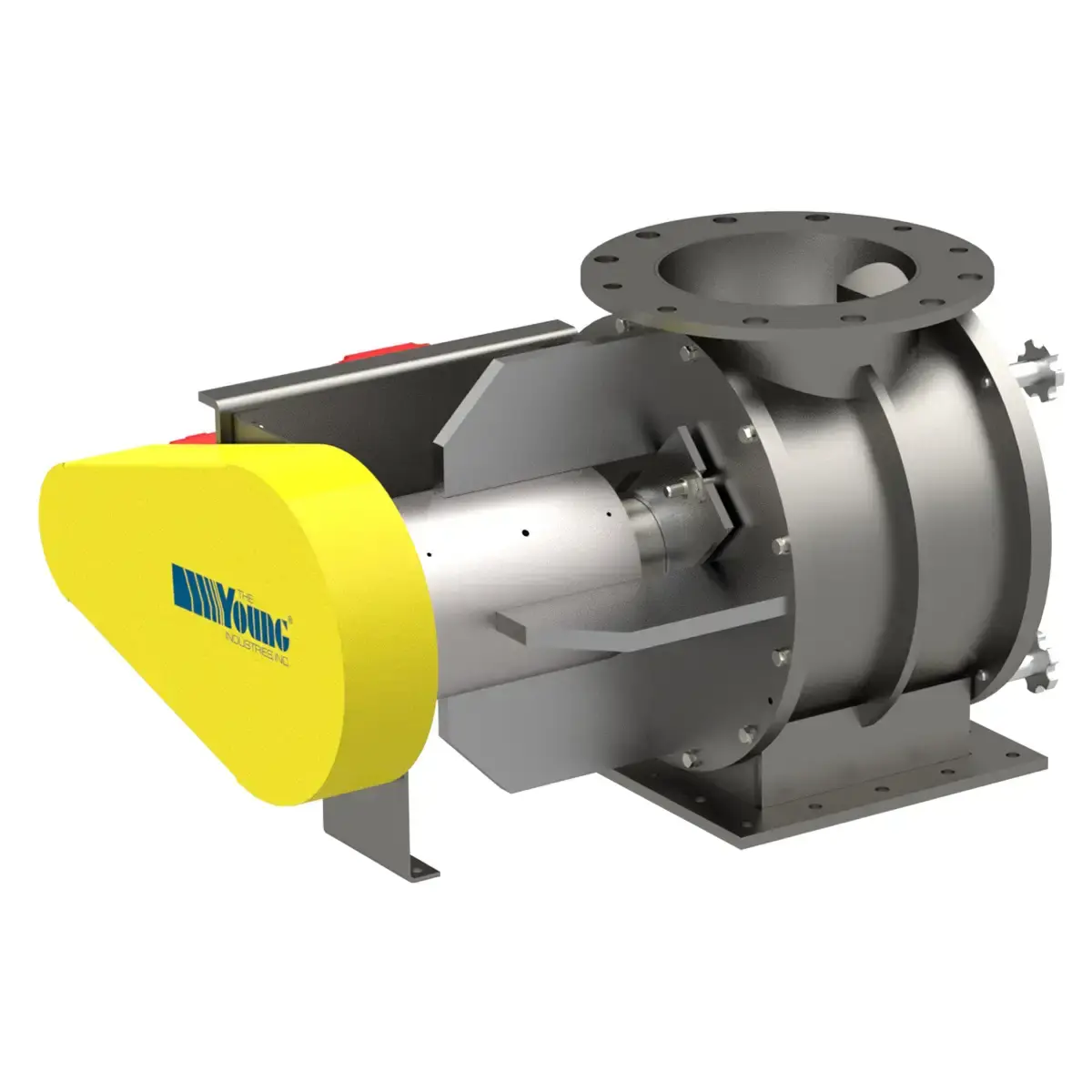
Model QC
Minimize downtime with Young Industries' Quick Clean Rotary Valves. Ideal for process applications demanding quick sanitation.
Learn More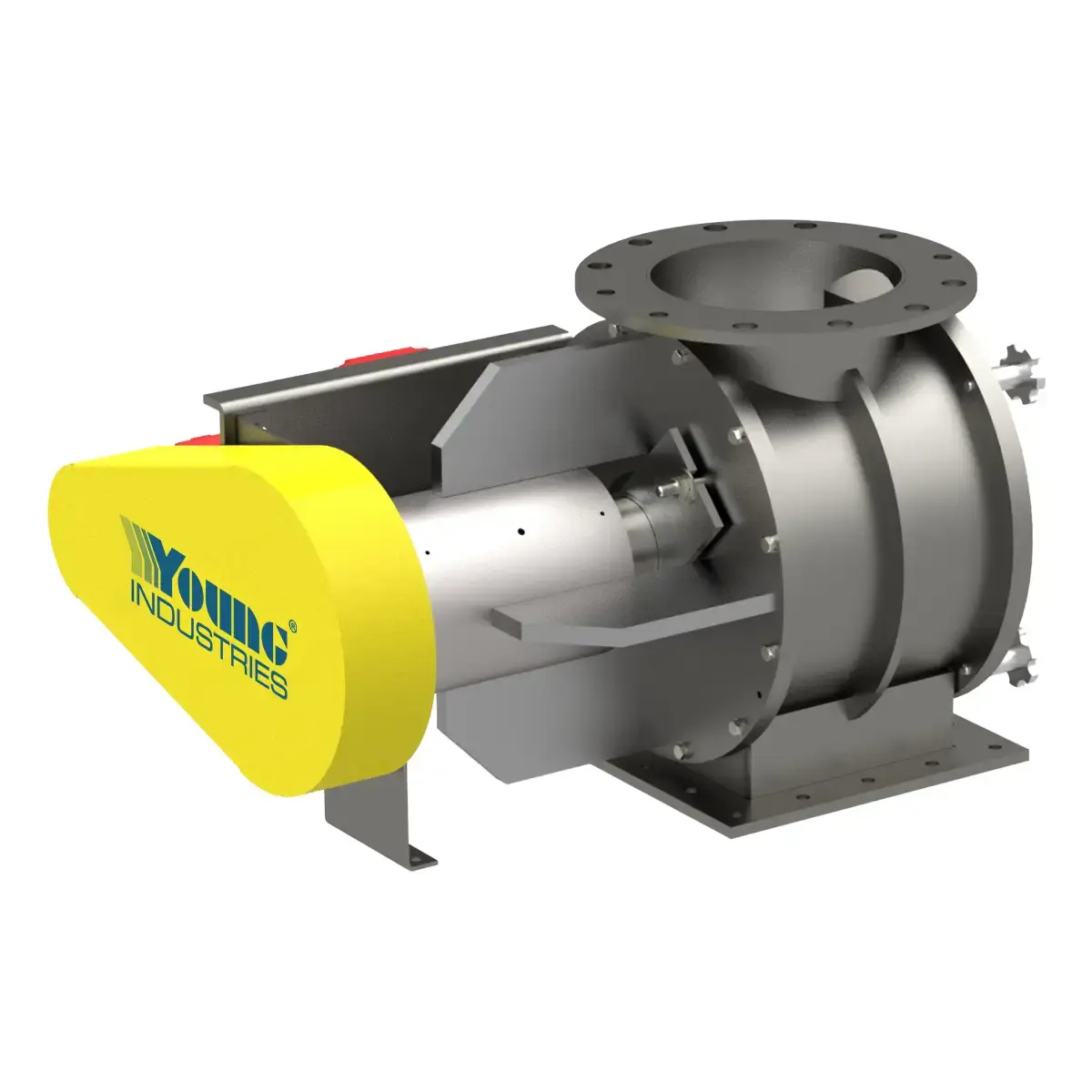
Model CA
Young Industries Cantilevered rotary valves offer a unique design for quick access for interior cleaning.
Learn More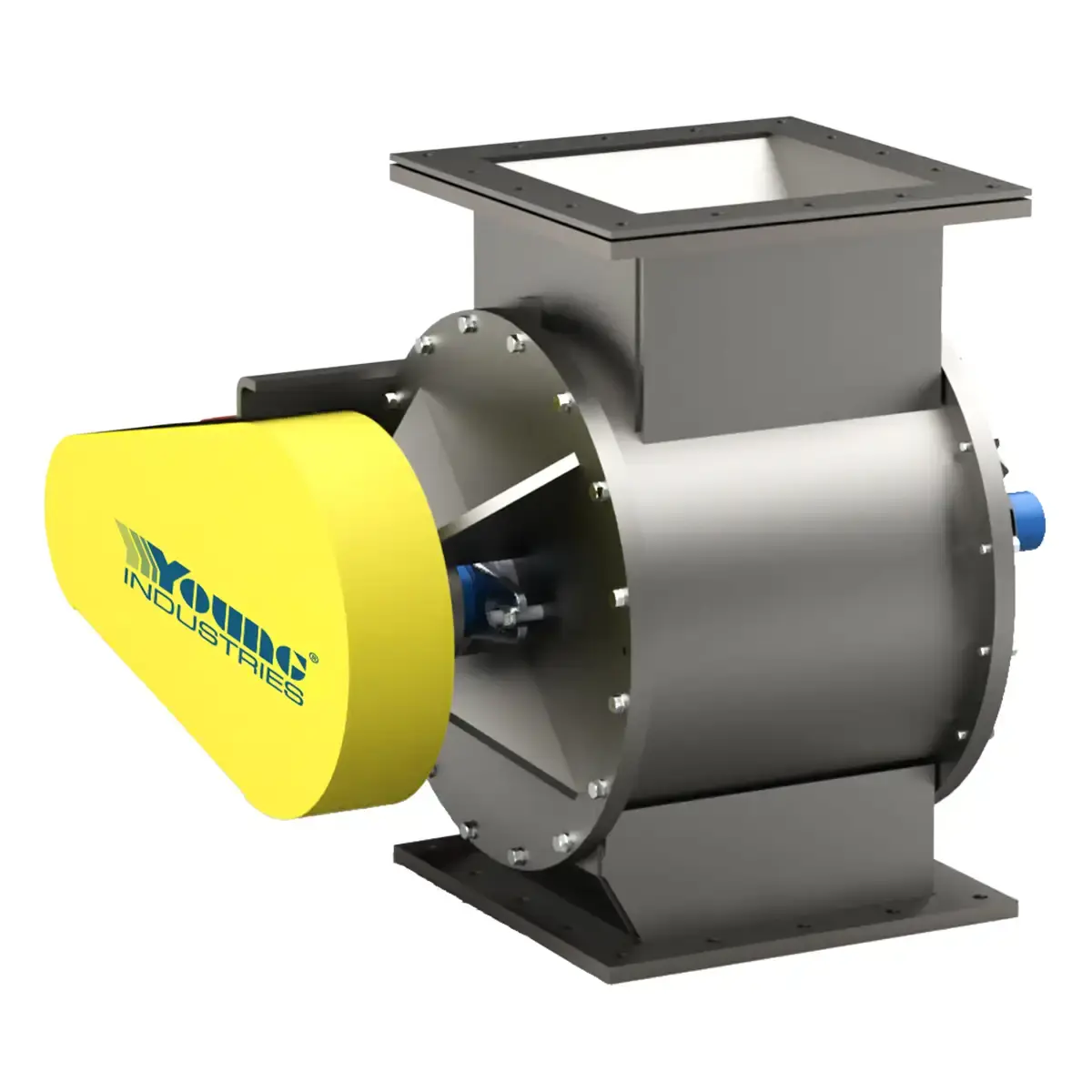
Model RNHC
The Young Industries RNHC Rotary Valve handles pellets up to 1/4" with minimal clipping for a smoother, more consistent flow and reduced downtime.
Learn More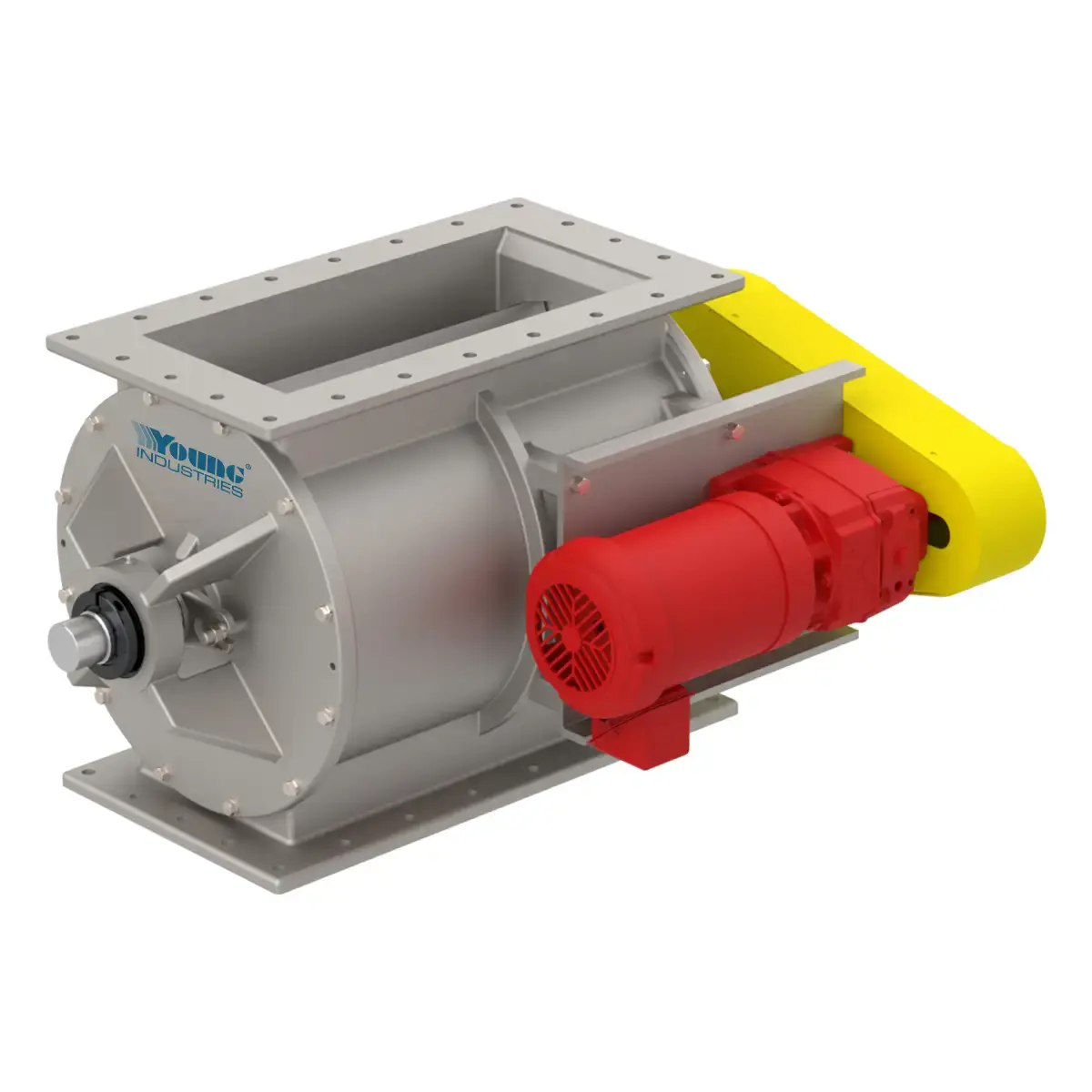
Model HC & LH
Extended Length Rotary Valves (LH, SE, HC) double capacity without increasing height. Perfect for applications with limited headroom and high throughput needs.
Learn More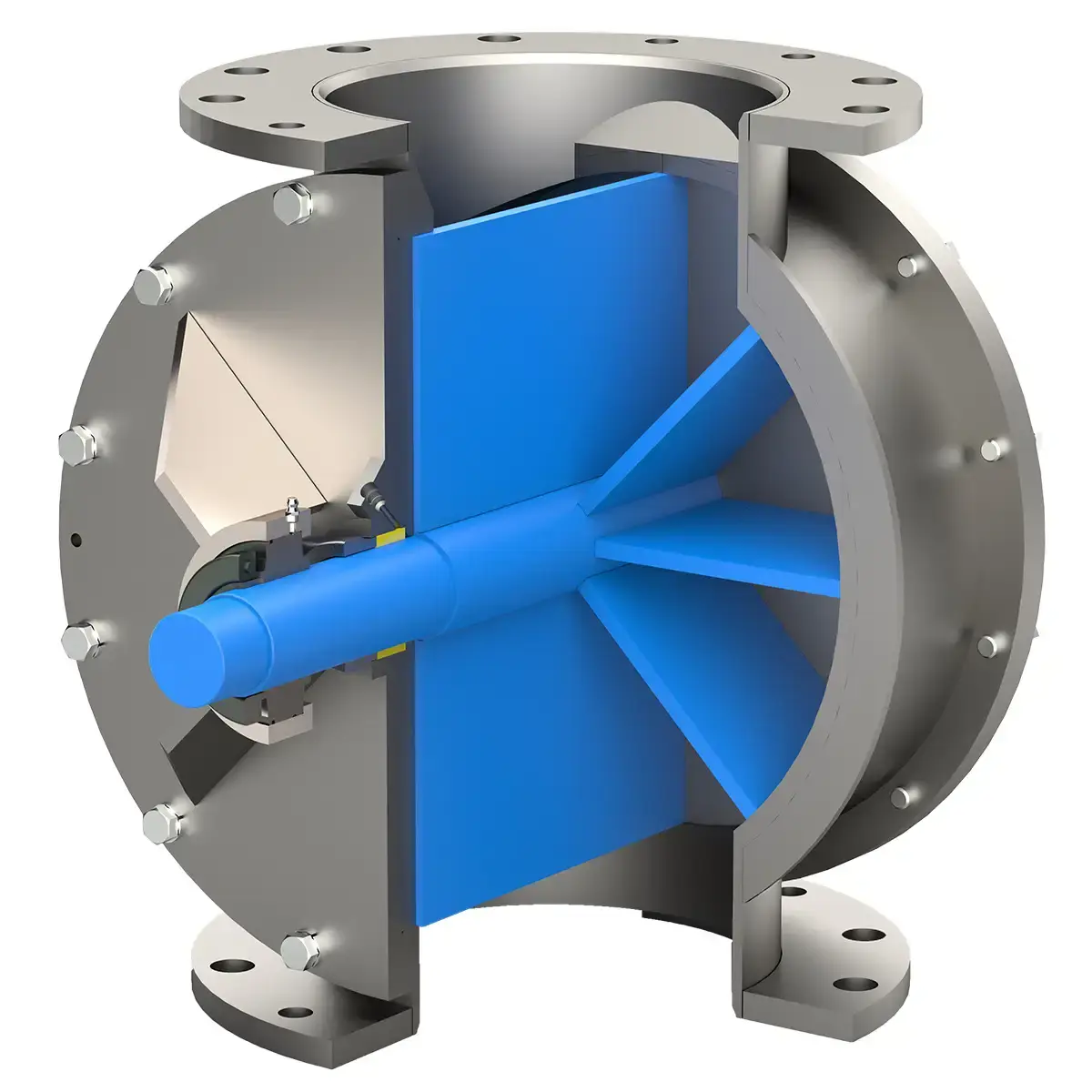
Model HC & LH
NFPA-compliant rotary valves offer safe, reliable powder handling. Expertly engineered to prevent deflagrations and meet your specific process needs.
Learn More